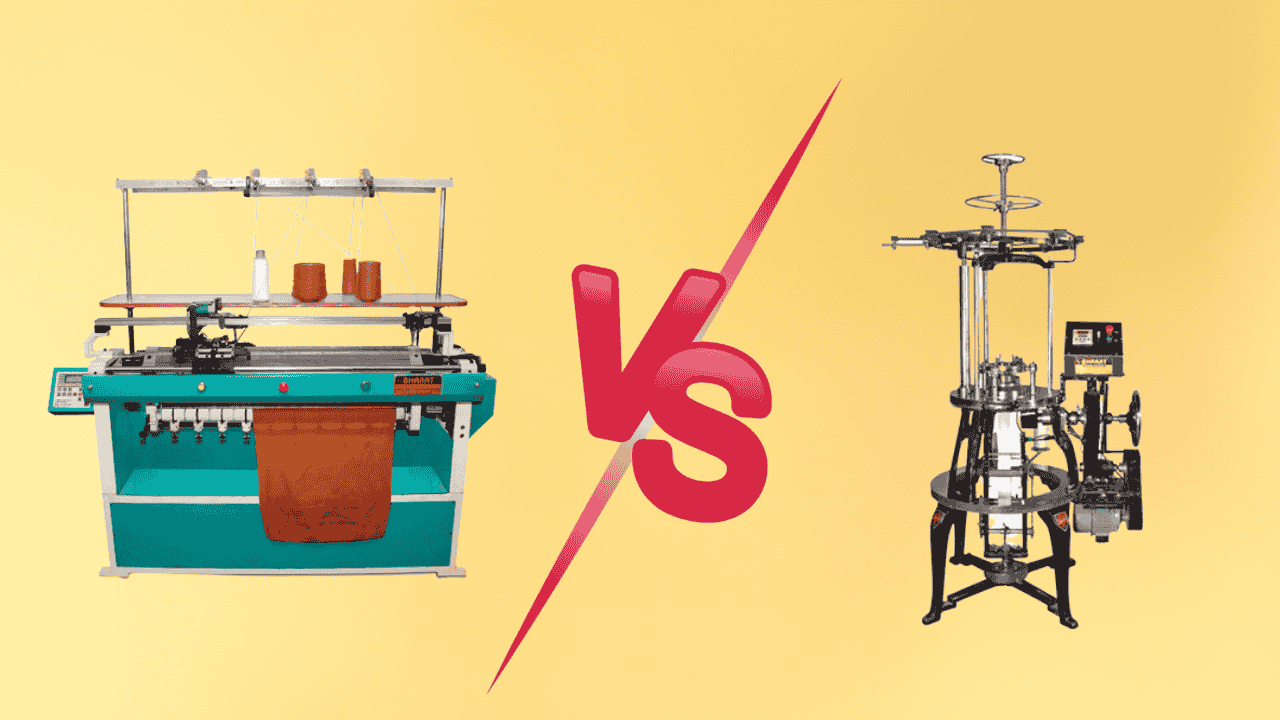
When it comes to industrial-scale fabric manufacturing, choosing the right knitting machine is essential. Two of the most commonly used types in commercial settings are flat knitting machines and circular knitting machines. While both are designed to create knit fabrics, they function differently and serve distinct production needs.
Here is a detailed comparison of Flat vs Circular Knitting Machine key features:
1. Knitting Structure and Machine Configuration
Flat Knitting Machines use a flat, horizontal needle bed. The carriage moves back and forth, allowing for more complex stitch patterns. These machines can produce both weft and warp knits, but are mainly used for weft knitting.
Circular Knitting Machines have a circular arrangement of needles on a rotating cylinder. As the cylinder turns, the fabric is knitted in a continuous spiral. These machines are optimized for high-speed weft knitting.
Key Use Case: Flat machines are ideal for structured garments and shaped components such as collars and sleeves, while circular machines are preferred for producing continuous tubular fabric in bulk such as t-shirts and seamless garments.
2. Fabric Output and Versatility
Flat machines can knit variable widths, make shaped panels, and support intarsia, jacquard, and transfer stitches, making them suitable for fashion garments and technical textiles.
Circular machines are more limited in stitch variety but can generate large volumes of single jersey, rib, or interlock fabrics efficiently.
Commercial Advantage: Flat knitting is often used in high-value, low-volume production. Circular knitting is used for mass production where speed and uniformity are priorities.
3. Production Speed and Efficiency
Flat knitting machines are slower due to the carriage movement and complexity of stitches.
Circular knitting machines operate at higher revolutions per minute, making them better suited for continuous, high-speed output.
Efficiency Note: Circular machines can produce hundreds of kilograms of fabric per day, making them essential in textile mills focused on bulk production.
4. Machine Control and Automation
Modern flat knitting machines offer advanced computer control for shaping and multi-color patterning.
Circular knitting machines also offer automation but are more focused on setting parameters for uninterrupted runs.
5. Fabric Form
Flat machines produce flat fabric panels, ideal for cut-and-sew or shaped knitting.
Circular machines produce tubular fabrics, which may require cutting and processing depending on the end use.
6. Application in Industry
| Feature | Flat Knitting Machines | Circular Knitting Machines |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Sweaters, panels, shaped garments | T-shirts, leggings, continuous yardage |
| Stitch Variety | High (intarsia, cable, tuck) | Limited (jersey, rib, interlock) |
| Speed | Moderate | Very high |
| Fabric Shape | Flat panels | Tubular rolls |
| Level of Detailing | Precise shaping and design | Uniform patterns |
Conclusion: Which Is Better for Commercial Use?
Both machines have their strengths depending on your manufacturing goals:
- If you are producing detailed, shaped knitwear or working in fashion or technical textiles, a flat knitting machine offers the flexibility and design control you need.
- If you are focused on high-volume garment manufacturing, especially for basic apparel or knitwear fabric rolls, a circular knitting machine will deliver better output and efficiency.
Understanding these core differences can help commercial textile businesses choose the right technology for scaling production while maintaining fabric quality.
Request a Free Consultation Today
Contact us today to get expert assistance, machine demos, or a custom quote. We’re here to help you boost your output and product quality with the best-in-class Bharat knitting machines.